[低端筆記] MIT算法導論 4. Heaps and Heap Sort
MIT的算法導論公開課有兩種版本, 我選較新版的
MIT 6.006 Introduction to Algorithms, Fall 2011
官方筆記
Heaps and heap sort (PDF)Priority Queues
一個各元素有其各自權重(key)的set S, 有以下幾種基本操作- insert(S, x)
- 將元素 x 插入 S 中
- max(S)
- return S 中最大值
- extract_max(S)
- return並移除 S 中最大值
- increase_key(S, x, k)
- 將 x 的權重提高為 k
- Decrease_key(S, x, k)
- 將 x 的權重降為 k
Heap
- Priority Queues的應用
- 為一組array, 可化成一棵nearly complete binary tree
- Max Heap Property
- 根結點 ≥ 子結點
- Min Heap則性質相反
Heap as a Tree
- the root of tree = array的第一個元素, i = 1
- parent(i) = i/2 //父節點
- left(i) = 2i //左子節點
- right(i) = 2i+1 //右子節點
- binary heap 高度為 O(lg n)
Heap Operations
- build_max_heap
- 從一個unordered array建立Max Heap
- max_heapify
- 將Heap調整成Max Heap(解決不符Max Heap Property部分)
- correct a single violation of the heap property in a subtree at its root
- insert
- extract_max
- heapsort
Max_heapify
- Assume that the trees rooted at left(i) and right(i) are max-heaps
- 若 A[i] 不符Max Heap Property, 則向下交換較大值直到符合
Max_heapify(A, i)
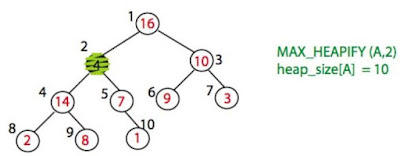 |
| A[2]不符, call Max_heapify(A, 2) |
 |
| A[2]與A[4]互換, A[4]不符, call Max_heapify(A, 4) |
 |
| A[4]與A[9]互換, 符合Max Heap |
Pseudocode
l = left(i)
r = right(i)
if(l <= heap-size(A) && A[l]>A[i])
then largest = l
else largest = i
if(r <= heap-size(A) && A[r]>A[largest])
then largest = r
if(largest!=i)
then exchange A[i] and A[largest]
Max_heapify(A,largest)
build_max_heap
將 A[1...n] 轉換為max heapPseudocode
Build_Max_Heap(A):
for i=n/2 downto 1
do Max_Heapify(A, i)
為什麼從n/2開始?
因為A[n/2+1...n]均為leaves → 符合左右子樹均為max-heaps複雜度:
O(n log n) via simple analysis
實際上為 O(n),
因為leaves上一層節點所需為 O(1), 依此類推, 上l層所需為O(l)
而上一層有n/4個節點, 上上一層有n/8...
→ n/4 (1 c) + n/8 (2 c) + n/16 (3 c) + ... + 1 (lgn c), 設n/4 = 2^k
→ c 2^k( 1/2^0 + 2/2^1 + 3/2^2 + ... (k+1)/2^k )
→ O(n)
Heap-Sort
- 從unordered array建Max Heap
- 找出最大元素A[1]
- Swap elements A[n] and A[1]
- 最大值移至array末端
- 將node n輸出到sorted array並從Heap移除
- 降低heap-size
- 跑max_heapify
- 雖然因為A[n]跟A[1]swap可能導致不符特性, 但左右皆為Max Heap, 故只須max_heapify修正
- Goto #2 直到heap清空
複雜度:
n*O(log n) → O(n log n)

![[低端筆記] MIT算法導論 4. Heaps and Heap Sort [低端筆記] MIT算法導論 4. Heaps and Heap Sort](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjursjCHRbsvYpPUaj1XpAyEBzOZnr1eWRcI0iwvFyNud6Hdk_Mhj9dgu6xcfsk6a39BGCLDepMY01aj7NNuLxfXUPpqAWyjbqH6YVIEEPvZujgMF5dQK3uz5_2ah1ooRLWhLU4LwPdPx8/s1600/6-006f11.jpg)


沒有留言:
張貼留言